Waste screening is a core step in the resource utilization of construction and municipal solid waste, and the scientific matching of supporting equipment directly determines screenin
g efficiency, resource recovery rate, and environmental compliance. Currently, some waste treatment projects suffer from low screening accuracy, frequent equipment failures, and high risks of secondary pollution due to improper selection and insufficient coordination of supporting equipment. This article systematically analyzes the functions, selection points, and application scenarios of various supporting equipment such as feeding, crushing, magnetic separation, and air separation, focusing on the entire process of "pretreatment - screening - post-treatment - auxiliary support." It provides standardized references for equipment configuration in waste screening production lines, helping to achieve the goals of "reduction, resource recovery, and harmless treatment" of waste and promoting the high-quality development of the environmental protection industry.
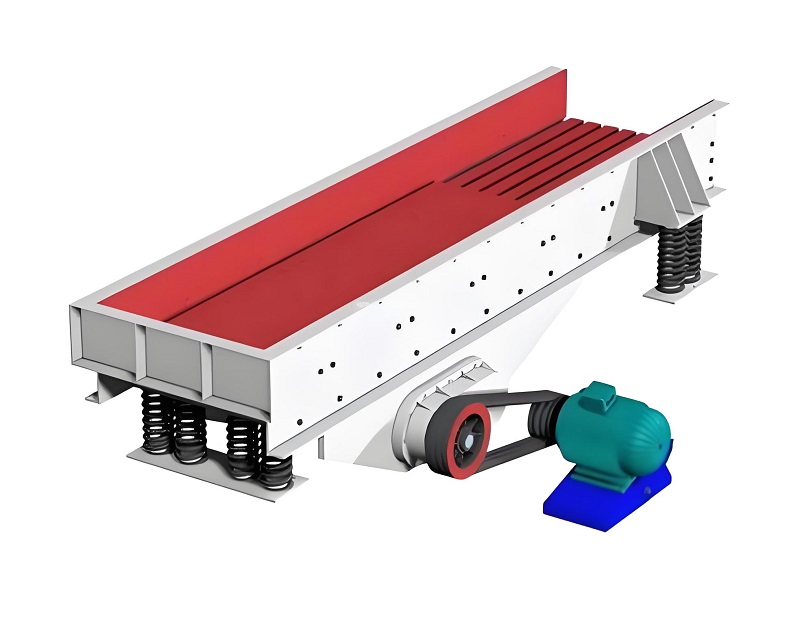
A. Pretreatment Supporting Equipment: Laying a Solid Foundation for Screening Efficiency
The core function of pretreatment equipment is to remove large impurities from waste, reduce humidity, and separate magnetic substances to avoid affecting the operation of screening equipment and improve subsequent screening accuracy.
1. Feeding Equipment: A "Stabilizer" for Uniform Material Supply Commonly used equipment includes vibrating feeders and belt feeders. Their core function is to uniformly and continuously convey waste to the screening equipment, preventing screen blockage or incomplete screening due to inconsistent feed amounts. Vibrating feeders generate vibration through an exciter, causing the material to slide evenly along the trough. They are suitable for sticky waste with high moisture content, with a processing capacity of 10-500 t/h. The feeding speed can be adjusted via frequency converter. Belt feeders are suitable for conveying large pieces of waste (particle size ≤ 500mm), with a conveying distance of 10-30m. When paired with a belt scale, they can achieve quantitative feeding, ensuring the screening equipment load remains stable at 75%-90% of its rated power. When selecting a model, the equipment specifications should be matched to the waste processing capacity. For example, a waste screening line with a daily processing capacity of 1000 tons should use a GZD-1500×6000 vibrating feeder with a 15kW motor to meet continuous feeding requirements.
2. Crushing Equipment: The "Pre-treatment Specialist" for Volume Reduction and Quality Improvement For large pieces of waste (such as furniture and construction waste), crushers (jaw crushers, hammer crushers, and shear crushers) are required to break them down, controlling the particle size within the feed requirements of the screening equipment (usually ≤300mm). Shear crushers use a dual-shaft shearing principle and are suitable for processing mixed waste containing metal and plastic, with a crushing ratio of 10-20, avoiding damage to the equipment from hard impurities. Hammer crushers are suitable for crushing brittle materials (such as bricks and ceramics), with a processing capacity of 50-300t/h, producing uniform particle size after crushing. For example, in a construction waste screening line, a jaw crusher is responsible for coarse crushing (breaking materials larger than 500mm into those smaller than 200mm), while a hammer crusher is responsible for medium crushing, ensuring that the particle size of the material entering the drum screen meets the requirements, improving screening efficiency by more than 30%.
3. Magnetic Separation Equipment: The "Safeguard" for Iron Removal and Screening Machines Magnetic materials such as reinforcing bars and iron wires in waste can easily entangle and damage screening equipment, requiring pre-separation by magnetic separators. Commonly used equipment includes suspended magnetic separators and drum magnetic separators, with magnetic field strengths of 8000-12000GS and magnetic material recovery rates exceeding 95%. Suspended magnetic separators are installed above the feeder or belt conveyor, suitable for pre-processing large pieces of waste, and can separate magnetic materials with a particle size ≥5mm. Drum magnetic separators are integrated with the belt conveyor and are suitable for removing iron from fine-particle waste (particle size ≤50mm), preventing magnetic impurities from entering subsequent screening stages. In municipal solid waste screening lines, magnetic separators can reduce screen entanglement failures, increasing equipment uptime by 25%.
4. Drying Equipment: The "Dryer" for Moisture and Clog Prevention For sticky waste with a moisture content exceeding 15% (such as kitchen waste and wet sludge), a dryer is required to reduce moisture and prevent material adhesion and clogging of the screen. Commonly used rotary drum dryers employ coal, gas, or electric heating methods, achieving drying temperatures of 80-120℃ and processing capacities of 20-200 t/h. They can reduce the moisture content of waste to below 10%. The dryer is linked to the screening equipment, using humidity sensors to monitor material moisture in real time and automatically adjust drying time to ensure smooth screening. For example, in a kitchen waste screening line, the dryer reduces material stickiness, lowering the screen clogging rate from 40% to below 5%.
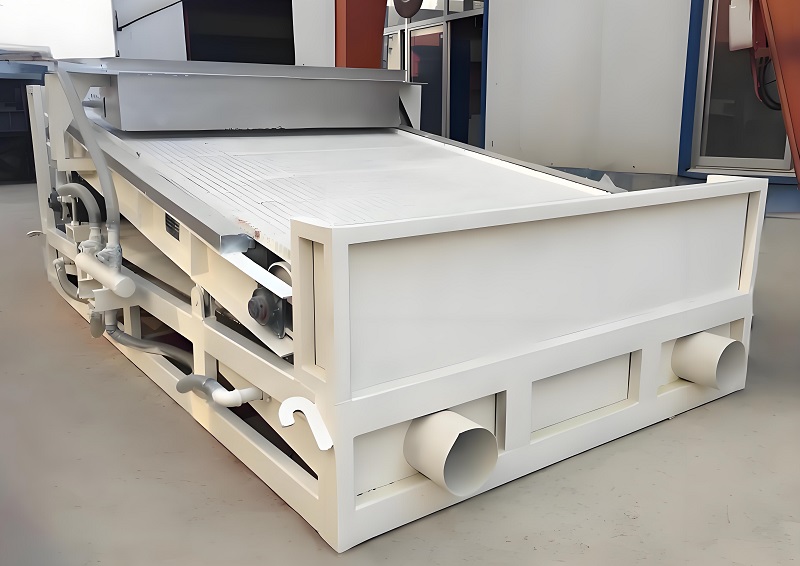

B. Core Screening Supporting Equipment: "Key Assistants" for Precise Grading This type of equipment works in conjunction with the main screening machine (rotary drum screen, vibrating screen) to improve grading accuracy, expand screening functions, and adapt to diverse waste treatment needs.
1. Grading and Screening Equipment: "Supporting Screens" for Fine Separation After the main screening machine completes coarse grading, it needs to be paired with multi-layer vibrating screens and high-frequency screens for fine grading, achieving separation of waste into multiple sizes. The vibrating screen uses a multi-layer screen (2-4 layers) to separate multiple particle size grades such as 0-5mm, 5-10mm, and 10-20mm, with a grading accuracy error of ≤3%. It is suitable for fine screening of recycled aggregates and organic fertilizer raw materials. The high-frequency screen has a vibration frequency of 1500-3000r/min, breaking down the stickiness of materials through high-frequency vibration. It is suitable for screening fine-particle waste (particle size ≤5mm) with a processing capacity of 10-100t/h. In the construction waste recycling production line, the drum screen and the three-layer vibrating screen are used together to produce three products in one go: recycled aggregate, bedding material, and backfill material, increasing the resource recovery rate to 85%.
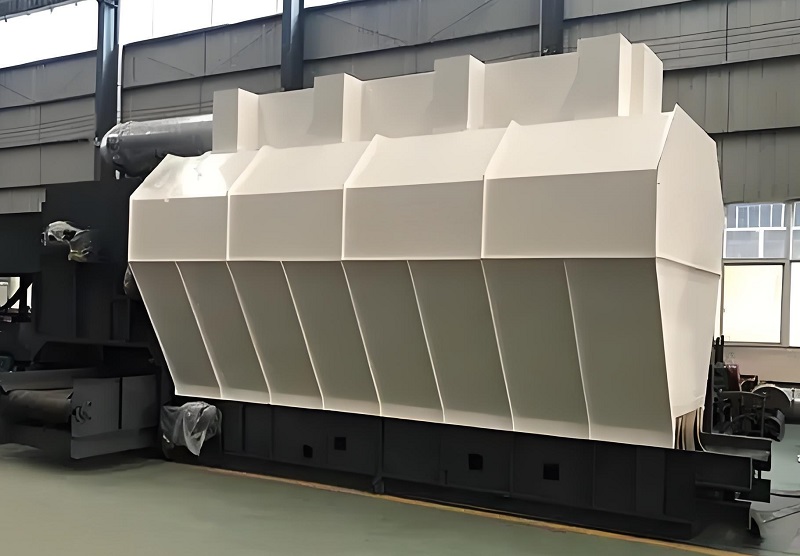

2. Air Separation Equipment: The "Sorting Expert" for Light and Heavy Material Separation. Used to separate light materials (plastics, wood chips, paper) and heavy materials (sand, gravel, metal) in waste. Commonly used equipment includes horizontal and vertical air separators. Horizontal air separators use a fan to generate horizontal airflow, separating materials based on density differences. Light materials can be recovered up to 90%, making them suitable for municipal solid waste and kitchen waste treatment. Vertical air separators employ a vertical airflow design, offering higher separation precision and the ability to distinguish materials with similar densities (such as PP and PE plastics). Air separators can be used in series with screening equipment; for example, fine particles separated by a drum screen can be further separated into recyclable materials like plastics and paper by the air separator, while heavier materials proceed to subsequent crushing, improving resource recovery efficiency.
3. Eddy Current Separator: A Powerful Tool for Recovering Non-Ferrous Metals For non-ferrous metals such as copper and aluminum in waste, eddy current separators are used for recovery. These separators utilize electromagnetic induction to generate eddy currents, pushing the non-ferrous metals away from the material flow and separating them from non-metals. The separators have a processing capacity of 50-200 t/h, a non-ferrous metal recovery rate of over 85%, and are suitable for materials with a particle size of 5-50 mm. In electronic waste sorting lines, eddy current separators can recover copper wires, aluminum casings, and other materials from the crushed waste, creating additional economic benefits for enterprises while reducing environmental pollution.
C. Post-processing Supporting Equipment: Achieving Resource Recovery and Harmlessness
Post-processing equipment is responsible for recycling or harmlessly treating different components after screening, achieving the goals of "reduction, resource recovery, and harmlessness" of waste.
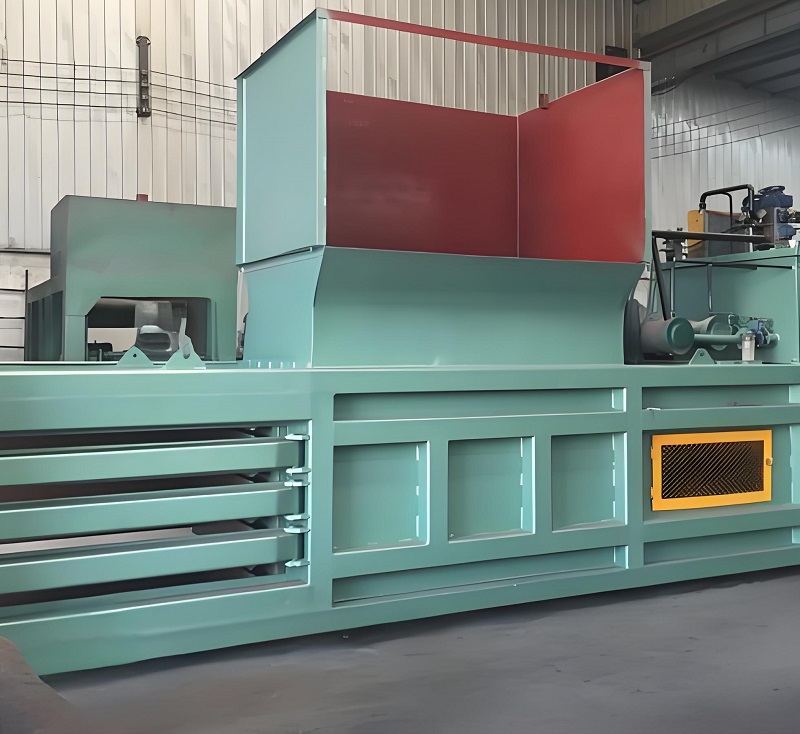

1. Conveying Equipment: The "Transport Link" for Material Flow
Including belt conveyors, screw conveyors, and scraper conveyors, used to connect various processing stages and achieve efficient material flow. Belt conveyors are suitable for long-distance conveying (5-50m), with a conveying capacity of 10-1000t/h. They can be installed at an incline (angle ≤18°) and are suitable for large, heavy materials. Screw conveyors are suitable for conveying fine particles and sticky materials (such as kitchen waste and sludge). Their sealed design prevents odor diffusion, and the conveying length is ≤15m. Scraper conveyors are suitable for high-temperature, dusty environments (such as conveying before waste incineration). They can be used horizontally or vertically, with a conveying capacity of 20-300t/h. Selection should be based on the material characteristics and conveying distance. For example, screw conveyors are suitable for screened kitchen waste to avoid leakage and environmental pollution.
2. Compression and Baling Equipment: The "Compressor" for Recycling Reduction For screened recyclable materials (plastics, paper, metal), compression and baling machines are needed to compress and bale them, reducing storage space and transportation costs. Hydraulic balers are hydraulically driven, with a baling pressure of 10-30 MPa, compressing loose materials into bales with a density of 0.8-1.2 t/m³, achieving a baling efficiency of 1-5 bales/minute. For example, after compression and baling, the transportation cost of recycled plastic bottles is reduced by 40%, and subsequent recycling is easier; baled metal scrap can be directly sold to steel mills, improving recycling convenience.
3. Harmless Treatment Equipment: A Guarantee of Environmental Compliance This includes deodorization equipment, dust removal equipment, and wastewater treatment equipment to ensure that the screening process meets environmental standards. The deodorization equipment employs a combined process of "biological filter + activated carbon adsorption," effectively removing odorous gases such as hydrogen sulfide and ammonia. It handles air volumes of 1000-10000 m³/h, controlling odor concentrations below national standard limits. A pulse dust collector treats dust generated during the screening process, achieving a dust removal efficiency of over 99.5%, with dust emission concentrations ≤10 mg/m³. The wastewater treatment equipment utilizes a "bar + flotation + biochemical treatment" process to treat screening wastewater (such as screen rinsing wastewater), achieving a COD removal rate ≥80%. The treated water can be recycled or discharged in compliance with standards. In urban solid waste screening centers, this type of equipment significantly improves the surrounding environment and enhances resident satisfaction.
D. Auxiliary Support Equipment: Ensuring Stable System Operation
Although auxiliary equipment does not directly participate in screening, it is crucial for the continuous operation of the production line. This includes control systems, power supply equipment, and maintenance equipment.
Intelligent Control System: The "Brain" of Efficient Operation Utilizing a PLC control system, integrating sensors (temperature, humidity, material level, and current sensors) and a touchscreen, it achieves coordinated equipment control, real-time parameter monitoring, and fault early warning. For example, the material level sensor monitors the feed rate of the screening equipment and automatically adjusts the feeder speed; the vibration sensor monitors the screen's operating status, issuing an alarm when abnormal vibration occurs to remind staff to check; the energy consumption monitoring module calculates the energy consumption of each piece of equipment and optimizes operating parameters to achieve energy savings. The intelligent control system reduces manual intervention, increasing the production line's automation rate to over 80% and reducing downtime by 30%.
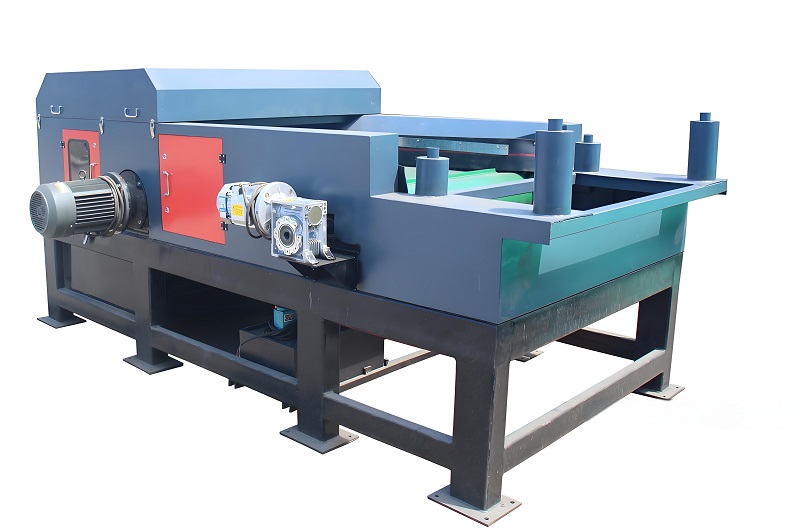
2. Power Supply and Lighting Equipment: The "Energy Source" for Stable Operation Equipped with transformers, distribution cabinets, and emergency generators, it ensures stable voltage (fluctuations ≤ ±5%), preventing equipment failures due to voltage fluctuations; explosion-proof lighting equipment is installed in the screening workshop and maintenance passages to meet operational and maintenance needs, with a brightness ≥ 200 lx. For waste treatment plants in remote areas, the emergency generator can ensure the operation of critical equipment (such as deodorization and dust removal equipment) during power outages, preventing environmental pollution. 3. Maintenance and Safety Equipment: The "Toolbox" for Operation and Maintenance Support
This includes cranes (electric hoists, truck cranes), maintenance platforms, fire-fighting equipment, and guardrails. Cranes are used for lifting components during equipment installation and maintenance. Electric hoists have a rated load of 2-10t and are suitable for replacing small components. Maintenance platforms are set around the screening equipment, with a height of 1.5-2m, facilitating staff inspection and replacement of screens. Fire-fighting equipment (fire extinguishers, fire hydrants) must be configured according to fire safety regulations, and guardrails and warning signs ensure operational safety. Comprehensive maintenance and safety equipment reduces maintenance difficulty and improves operational safety.
The efficient operation of waste screening relies on the coordinated efforts of all supporting equipment throughout the process. Pre-treatment equipment lays a solid foundation for screening, core supporting equipment improves grading accuracy, post-treatment equipment achieves resource recovery and harmless treatment, and auxiliary support equipment ensures system stability. Various types of equipment need to be precisely selected based on waste type, processing volume, and environmental protection requirements to form a complete system with complementary functions. Properly configuring supporting equipment can not only increase screening efficiency by more than 30% and resource recovery rate to 85%, but also effectively control pollution such as dust and odor. The equipment configuration schemes described in this article are both practical and targeted, providing scientific guidance for equipment selection and production line construction in waste treatment projects, and helping the industry reduce costs, increase efficiency, and achieve green transformation.
Save Time! Get A Detailed Quotation Quickly.
