With the accelerating pace of urbanization, the amount of urban waste generated continues to rise. Large quantities of aged waste accumulate or are landfilled, not only consuming valuable land resources but also easily causing soil, groundwater, and air pollution, threatening the ecological environment and human health. Aged waste is complex in composition, high in moisture content, and severely mixed, making screening, a core prerequisite for its resource utilization and harmless treatment, far more challenging than for ordinary construction waste. Air separators, relying on aerodynamic principles and their high efficiency in separating lightweight materials, play an irreplaceable role in aged waste screening. They can achieve precise separation of materials of different densities, facilitating the reduction, resource recovery, and harmless treatment of aged waste, providing strong support for solving the challenges of aged waste disposal.
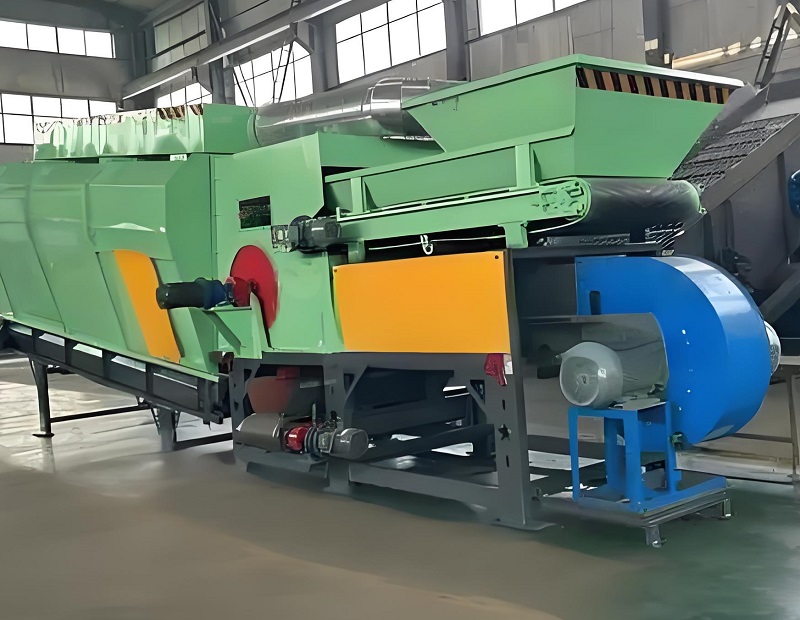

The core application of air separators in aged waste screening is to achieve efficient separation of lightweight combustible materials from heavy, inert materials, taking into account the characteristics of aged waste. This is also its core advantage in adapting to aged waste treatment scenarios. Stale waste is mostly a mixed waste accumulated over many years, containing lightweight combustible components such as plastics, textiles, wood chips, and paper scraps, as well as heavy, inert components such as sand, bricks, tiles, glass, and metals. It also contains a large amount of humus and sewage, resulting in a chaotic and heavily clump-bound composition. Unlike ordinary waste, the lightweight materials in stale waste are prone to aging and breakage after long-term accumulation, while the heavy materials are easily encased in humus. Traditional screening equipment struggles to achieve effective separation. However, air separators, through the buoyancy and wind force generated by directional airflow, can accurately distinguish materials of different densities, achieving efficient sorting and clearing obstacles for subsequent classification and resource utilization.
Air separators can accurately separate lightweight combustible materials from stale waste, providing high-quality raw materials for waste-to-energy incineration and improving energy recovery rates. Lightweight components in stale waste, such as plastics, textiles, and waste wood, have high calorific values and are ideal raw materials for incineration power generation. However, if these materials are mixed with heavy, inert materials, it will reduce incineration efficiency, increase incinerator wear, and may also produce harmful gases due to incomplete combustion. Air separators, by adjusting the airflow speed to suit aged waste, can blow up and collect lightweight combustible materials with lower density, effectively removing heavy impurities such as sand, gravel, and bricks, thus improving the purity and calorific value of the combustible materials. The lightweight combustible materials treated by air separation have significantly improved incineration efficiency, not only increasing power generation but also reducing pollutant emissions during incineration, transforming aged waste from "pollutants" into "energy," achieving energy resource recovery.
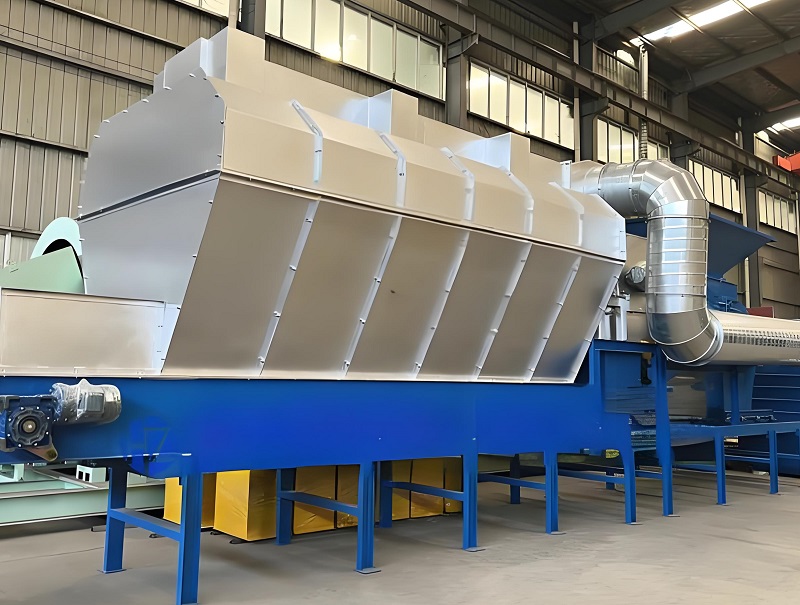

Separating heavy, inert materials and promoting their resource regeneration, realizing "turning waste into treasure," is another important application of air separators in aged waste screening. Heavy, inert materials such as sand, gravel, bricks, and glass in aged waste are chemically stable and not easily decomposed. After separation and purification, they can be recycled. However, these materials are often encased in humus and lightweight waste, making direct recycling difficult. Air separators separate lightweight materials while allowing denser, inert materials to settle under gravity. After simple washing and screening, these materials can be processed into recycled aggregates for roadbed paving and eco-friendly brick production, replacing traditional sand and gravel resources. Materials such as glass and metal can be directly recycled and reprocessed after further sorting, reducing resource waste and practicing the "reduction and recycling" treatment philosophy.
Air separators effectively remove lightweight floating impurities from aged waste, optimizing subsequent landfill treatment and reducing environmental pollution risks. For aged waste components that cannot be incinerated or recycled, safe landfill treatment is necessary. However, if this type of waste contains a large amount of lightweight floating material, it is easily washed away by rainwater and blown by wind after landfilling, causing the waste to scatter and pollute the surrounding soil and water bodies. At the same time, lightweight materials are difficult to compact after landfilling, increasing landfill space and shortening landfill lifespan. Air separators can pre-separate and remove these lightweight floating impurities, reducing the lightweight components in landfill waste, making it easier to compact, improving landfill space utilization, and preventing secondary pollution caused by the scattering of lightweight waste. This reduces environmental risks during the landfill process and ensures the safety of the surrounding ecological environment.
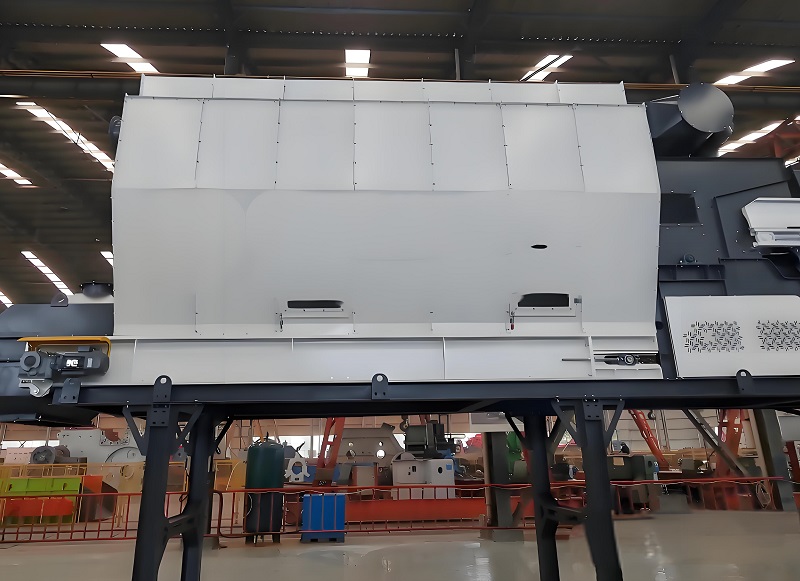

Compared to traditional manual sorting and single screening equipment, air separators are suitable for screening aged waste, significantly improving screening efficiency and reducing processing costs and labor intensity. Aged waste has a pungent odor and produces a lot of wastewater. Manual sorting is not only inefficient but also poses serious health risks to workers, and the sorting accuracy is difficult to guarantee, easily resulting in missed or incorrect selections. Air separators can achieve continuous automated operation without direct human contact with waste, effectively avoiding operational risks. At the same time, the screening efficiency far exceeds that of manual sorting, enabling the rapid processing of large quantities of aged waste and shortening the processing cycle. Furthermore, the air separator boasts a simple structure and convenient operation. It can flexibly adjust the air speed according to changes in the composition of aged waste, adapting to the screening needs of different batches and compositions of aged waste, reducing equipment failures and lowering equipment maintenance and labor costs.
The air separator can also help optimize the aged waste processing flow, improving the stability and processing efficiency of the entire production line. The core process of aged waste processing is "crushing—screening—sorting—processing." The air separator can seamlessly connect after the crusher and vibrating screen, forming a continuous processing flow. Aged waste after crushing and screening directly enters the air separator for sorting, eliminating the need for additional transfer and reducing material loss and secondary pollution during transport. Simultaneously, the air separator can separate most of the light and heavy materials in advance, reducing the load on subsequent sorting and processing equipment, minimizing equipment wear, improving the processing efficiency and stability of the entire production line, ensuring the orderly progress of aged waste processing, and achieving the dual goals of harmless and resource-based disposal.
Air separators are widely used and crucial in the screening of aged waste. Their core function is to precisely separate lightweight combustible materials from heavy, inert materials using aerodynamic principles. They not only provide high-quality feedstock for incineration power generation and promote the recycling of heavy materials, but also optimize landfill treatment, reduce environmental pollution, and significantly improve screening efficiency while lowering processing costs. This addresses the challenges of complex composition and difficult screening of aged waste. With increasingly stringent environmental policies and rising demands for aged waste treatment, the application of air separators will become more widespread, and their technology will continue to upgrade, providing strong support for the harmless disposal and resource utilization of aged waste, thus contributing to ecological environmental protection and sustainable development.
Save Time! Get A Detailed Quotation Quickly.
